In our modern society, effective weight management methods are a priority for individuals. Be it a busy lifestyle, inadequate physical activity, unhealthy dietary choices, or even certain health issues, it is undeniable that obesity has become a widespread epidemic. For some people, making use of a diet and exercise plan is not quite as easy as it sounds, and this is where weight loss medication comes into play.
If you are contemplating medication as an aid to weight loss, it is essential to grasp the steps involved, safety precautions, and the categories of drugs that are available. In this in-depth guide, we will discuss how to obtain weight loss medication, including the medical prerequisites, how to approach your physician, prescription versus over-the-counter options, and other pertinent information.
1. Recognize What Are Weight Loss Medications

Anti-obesity agents, or weight loss medications, are used to help individuals shed pounds when lifestyle adjustments have not proved effective. Their mechanisms of action include:
- Suppressing appetite.
- Reducing fat absorption.
- Increasing satiety.
- Metabolism enhancement.
Most anti-obesity medications are sanctioned by the FDA and are prescribed only after a thorough medical evaluation, especially for patients with a BMI (Body Mass Index) of 30 and above, or 27 and above with comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes or hypertension.
2. Check If You Are Eligible For Prescription Weight Loss Medication
Before pursuing anti-obesity drugs, consider whether you meet the criteria. Traditionally, evaluating this revolves around:
- BMI (Body Mass Index):
- BMI ≥ 30 (obesity)
- BMI ≥ 27 with risk factors (hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea)
- Previous weight loss efforts: A reasonable approach to weight management involves dieting, exercising, and if unsuccessful, medication.
- Relevant medical history: Metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and even PCOS may make you a candidate.
Important: Weight reductions are not to be taken lightly. Weight loss drugs are medically designed to aid those at risk due to obesity.
3. Consult a Healthcare Provider
The first step in acquiring weight loss medication is to speak with your doctor and/or a certified specialist in weight management. Here is some information to help you prepare:
- Medical History. Be prepared to share your entire medical history including any medications you currently take.
- Weight Loss History. Provide details on your attempts and results with lifestyle changes.
- Health Concerns. Report joint pain, fatigue, or trouble sleeping that may relate to your weight.
Your doctor may perform:
- Blood tests
- Thyroid screening
- Blood pressure and cholesterol evaluation
- Glucose or insulin testing
With the test results, your physician will assess whether you qualify for medication.
4. Types of Weight Loss Medications
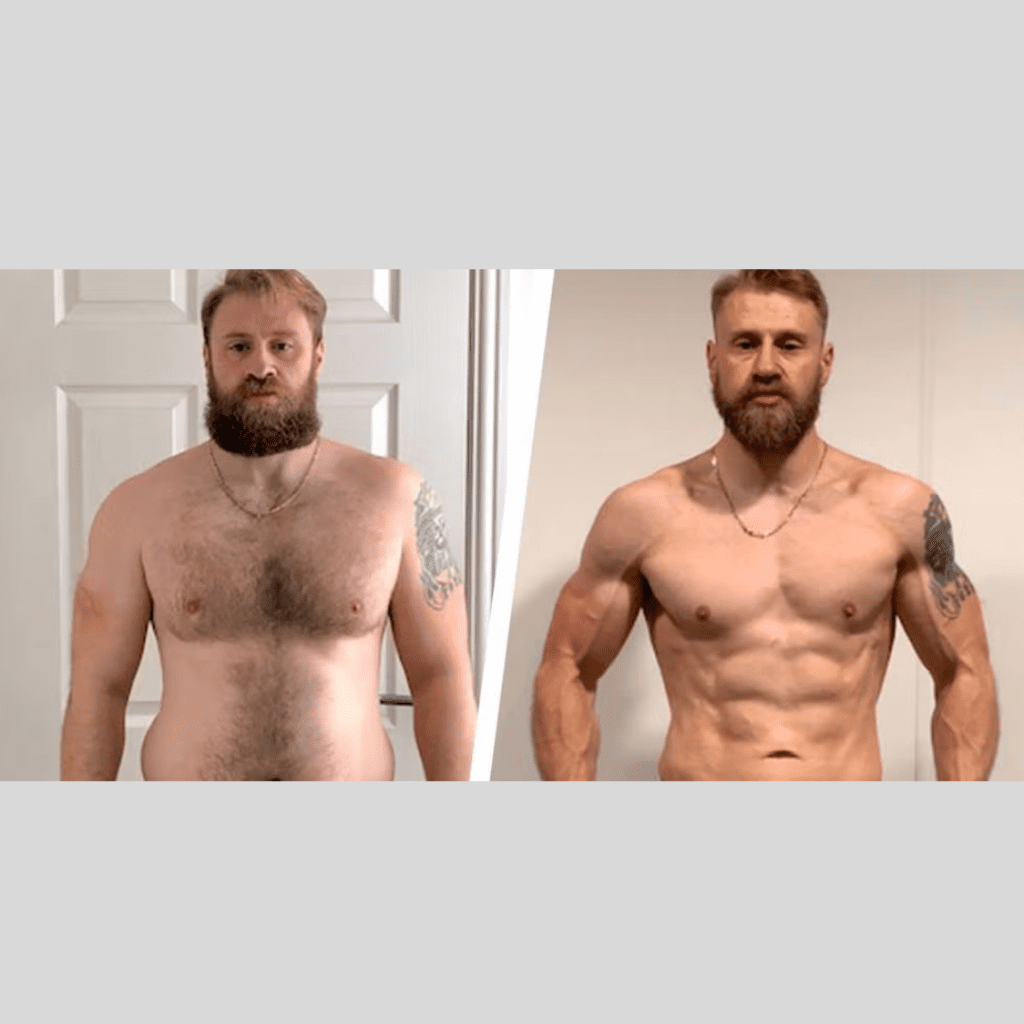

There are multiple drugs approved by the FDA for weight loss. Below are some of them with short explanations:
1. Orlistat (Alli, Xenical)
- Orlistat works by reducing fat absorption in the intestines.
- Available in prescription (Xenical) and over-the-counter (Alli) forms.
- Side effects: oily stools, gas, abdominal discomfort.
2. Phentermine-Topiramate (Qsymia)
- Appetite suppressant and energy expenditure stimulant.
- Only available via prescription.
- Common adverse effects: dry mouth, insomnia, dizziness, constipation.
3. Bupropion-Naltrexone (Contrave)
- Impacts neurogenic mechanisms of hunger and craving.
- Only available via prescription.
- Common adverse effects: nausea, headache, elevated hypertension.
4. Liraglutide (Saxenda)
- An injectable medication with indications for diabetes.
- Makes you feel satiated faster.
- Requires prescription.
- Common adverse effects: nausea, diarrhea, possible thyroid tumor risks.
5. Semaglutide (Wegovy, Ozempic)
- Developed initially for diabetes type 2.
- Administered as a weekly injection to modulate appetite-controlling peptides.
- Highly effective but requires a prescription.
- Common adverse effects: nausea, gastrointestinal discomfort.
Prior to taking any medication, it is crucial to speak with your physician about costs, availability, insurance coverage, and potential drug interactions.
Buy Mitolyn Supplement

5. Search for Online Weight Loss Clinics and Telehealth
For users who seek the convenience of online healthcare, telemedicine has simplified the process of obtaining prescription medication for weight loss.
Steps to follow:
- Search for a well-reviewed telehealth provider (e.g. PlushCare, Calibrate, Found, Ro).
- Complete a medical questionnaire.
- Attend a virtual consultation with an authorized medical professional.
- As soon as your prescription is approved, it can be sent to a pharmacy or shipped directly to you.
This method works best for semaglutide (Wegovy) and phentermine. Remember to verify that the platform is HIPAA-compliant and uses licensed practitioners.
6. Consider Over-The-Counter Options (With Caution)
Some weight loss aids are available over the counter, including:
- Orlistat (Alli)
- Fiber supplements
- Green tea extract
- Caffeine-based thermogenics
Despite these supplements being easily accessible, they are generally less effective than their prescription counterparts. They may also contain unregulated ingredients or hidden side effects. Always consult with a healthcare professional before taking these supplements.
7. Track Progress, Stay Engaged
Your treatment plan starts after the prescription of weight loss medication. These medications need to be complemented with a plan to be effective. For optimal results:
- Adhere to a nutritious diet regimen
- Remain active
- Monitor weight alongside body measurements
- Participate in scheduled follow-up appointments
Medications for weight loss are intended to be used in the short- to medium-term (3–12 months) unless otherwise directed. Your doctor will assess your current progress and revise the strategy when necessary.
8. Side Effects and Risks of Prescription Drug Use
All medications come with risk of side effects, including:
- Nausea
- Dry mouth
- Diarrhea or Constipation
- Increased heartbeat
- Changes of mood
While rare, some serious complications of these medications can include pancreatitis, liver damage, or other mental health concerns. Always inform your doctor about any unusual symptoms so they can be addressed right away.
Also, all drugs aimed for weight loss should never be taken by pregnant or breastfeeding women.
9. Check Insurance and Affordability Options
These medications can be extremely expensive, especially newer drugs like Wegovy or Saxenda which can cost over \$1,000 or more per month without insurance. These costs can be minimized by:
- Asking your doctor about generic alternatives
- Checking for manufacturer discount programs
- Seeing if their insurance covers obesity treatment
- Using prescription savings cards like GoodRx or SingleCare
Final Thoughts
Although medication can help you lose weight, remember it is not a cure. For long-term successful weight loss, partner with a qualified healthcare professional while remaining educated and committed to embracing a comprehensive strategy that encompasses nutrition, physical activity, and behavioral adjustments.